-
Class Summary Class Description SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2dengineSoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2dperforms the logical correlation between a binary image and a binary kernel.SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d.SbCorrelationDetail Results details of image correlation.SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2dengine TheSoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2dimage filter performs a correlation between a grey level image I and a grey level kernel K returning the correlation image O.SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.SbCorrelationDetail Results details of image correlation. -
Enum Summary Enum Description SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d.OffsetModes See Correlation.SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.CorrelationCriterions See Correlation.SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.CorrelationModes See Correlation and for eachSoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.CorrelationCriterion.SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.OffsetModes This field is ignored in the multiply correlation mode.
Package com.openinventor.imageviz.engines.geometryandmatching.patternrecognition Description
The correlation filters allow you to specify a correlation step.
The correlation filters allow the matching of rectangular or irregular patterns. Non-rectangular patterns are implemented with mask AOIs.
Use SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d for grayscale image correlation and SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d for binary image correlation.
SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d allows for local luminosity and / or contrast normalization. There are 4 different correlation types (see SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.CorrelationMode) :
- DIRECT: Direct correlation (no normalization).
- MEAN: Mean normalized correlation (luminosity).
- VARIANCE: Variance normalized correlation (contrast).
- MEAN_VARIANCE: Mean and variance normalized correlation (luminosity and contrast).
We perform the correlation between a 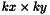 input image,
input image, 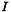 , and a
, and a 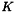 kernel,
kernel, 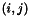 . The output image is an
. The output image is an 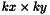 floating point image,
floating point image, 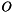 . The correlation coefficient at location
. The correlation coefficient at location 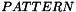 is given by a local calculation between the model and a pattern extraction from the input image,
is given by a local calculation between the model and a pattern extraction from the input image, 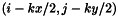 . The pattern location is
. The pattern location is 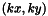 and its dimension is
and its dimension is 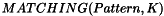 . The actual calculation depends on image type:
. The actual calculation depends on image type:
- logical for
SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d, - multiplication for
SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2dwithMULTIPLY, - difference
SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2dwithSUBSTRACTor - sign change criteria
SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2dwithSIGNCHANGE.
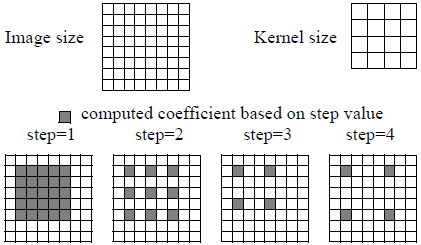
It also depends on the correlation normalization TYPE as shown below. When a part of the pattern lies beyond the edge of the image the correlation is not performed on the image border. SCorrelation filters provide a step parameter (see SoGrayscaleCorrelationProcessing2d.OffsetMode and SoBinaryCorrelationProcessing2d.OffsetMode) which speeds up the operation by calculating 1 value out of each step, as shown in Figure 1.
The luminosity and contrast normalization is controlled by one of the 4 correlation types:
- DIRECT: Direct correlation (no normalization).
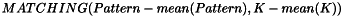
- MEAN: Mean normalized correlation (luminosity).
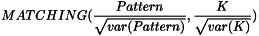
- VARIANCE: Variance normalized correlation (contrast).
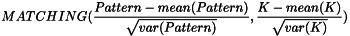
- MEAN_VARIANCE: Mean and variance normalized correlation (luminosity and contrast).
Output Image Normalization During the correlation the minimum and the maximum values are calculated
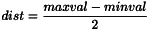 . At the end of the filter processus, the correlation image is normalized between -1 and 1. The normalization depends on the following algorithm:
. At the end of the filter processus, the correlation image is normalized between -1 and 1. The normalization depends on the following algorithm: 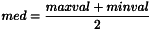
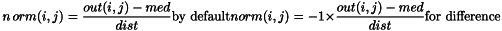
Position of the Correlation Coefficients If the dimensions are odd, the position of the correlation coefficient is centerd in the pattern and corresponds to a pixel position.
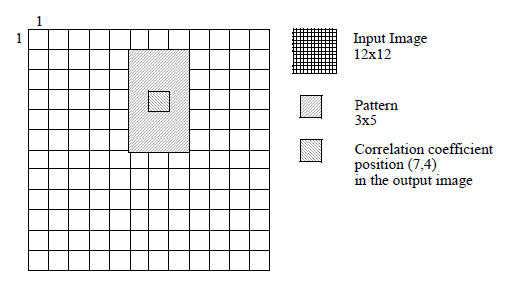 If the dimensions are even, the position of the correlation coefficient is the closest pixel position to the top and the left.
If the dimensions are even, the position of the correlation coefficient is the closest pixel position to the top and the left. 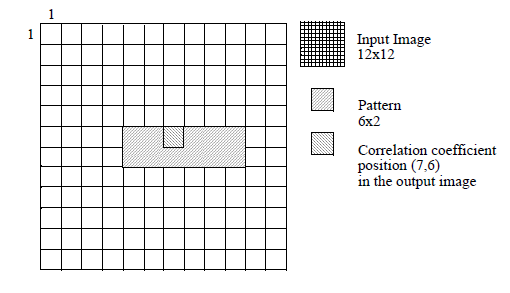
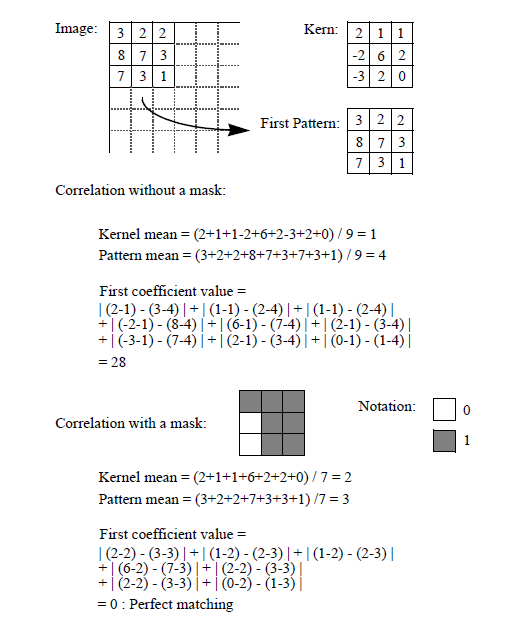
Correlation with a Non-Rectangular Pattern If a binary image is attached as a mask to the kernel image
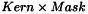 , the correlation is made locally between
, the correlation is made locally between 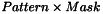 and
and 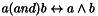 . The mean and variance calculation are made on
. The mean and variance calculation are made on 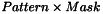 and on
and on 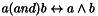 .
. 
Output Data The correlation filters return a floating point correlation image. At the end of the processus, this correlation image is converted between -1 and 1 (worst and best matching detected). The non-calculated points are set to -3e38. Then, the
SbCorrelationDetailcontains: - the position of the best matching (
matchingPositionX,matchingPositionY), - the minimum and the maximum values of the correlation image before the conversion (
minComputed,maxComputed), - the theoretical minimum and maximum correlation values before the conversion (
minTheoretical,maxTheoretical).